Researchers at MIT have created robots that may be used to construct new robots and objects a good deal large than themselves.
Researchers at MIT’s middle for Bits and Atoms are operating on an ambitious undertaking, designing robots that efficiently self-bring together. The crew admits that the purpose of a self-sustaining self-constructing robot is still “years away,” however the paintings have up to now established high-quality results.
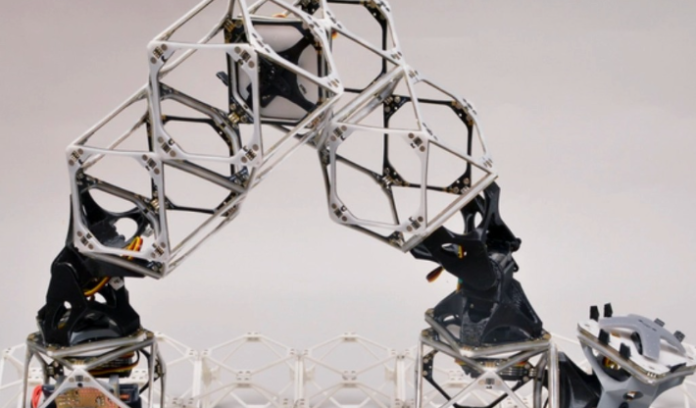
On the gadget’s middle are voxels (a term borrowed from laptop images), which convey electricity and facts that can be shared among portions. The portions shape the inspiration of the robotic, grabbing and attaching additional voxels earlier than moving across the grid for further meeting.
The researchers notice in an associated paper published in Nature, “Our technique demanding situations the convention that large structures need large machines to construct them, and might be implemented in areas that nowadays either require enormous capital investments for fixed infrastructure or are altogether unfeasible.

In latest years, we will have a look at the tremendous development of technology related to the control and optimization of labor in various industries. one each of them is robotics, which, thanks to the studies of scientists from the American Institute of an era in Massachusetts (MIT), controlled to create a robotic able to constructing different robots, editing its personal configuration and growing systems plenty large than itself.
The concept of the scientists is primarily based on the usage of so-referred to as voxels (3-dimensional equivalents of pixels in laptop images), i.e. smaller, unbiased components. And despite the fact that one of these answers has been known for a long term, scientists have advanced it, allowing man or woman elements now not handiest to attach in any manner, but additionally to transfer electricity and data between each other. way to this, it’s miles feasible not simplest to transport individual gadgets, but also to lift, lower, and manage them. one of the authors of the mission, Neil Gershenfeld, described this solution in the simplest way:
There aren’t any wires. there may be the most effective shape.

With the advent of such an innovative creation approach, scientists confronted new challenges. As they admit, the most important of them is the creation of an algorithm this is capable of deciding whether or not it will likely be more efficient to create a given shape via a robot in its cutting-edge shape all through the development of an object, or if it is higher to rebuild it. this is how Gershenfeld describes the trouble:
heaps of articles were posted on robot path-making plans. however the step wherein the robotic has to determine whether to construct some other robotic or every other sort of robotic is new.












[…] Scientists have high expedients for a bitsy glass tube robot in perfecting the capabilities and safety of robots used in non-invasive microsurgeries. […]
[…] in the field of assistive robotics, for case in prosthetics, fastco-adaptation of mortal and machine isn’t yet common. […]
[…] Soft robots is a burgeoning field combining electrical engineering and accoutrements wisdom to produce robots that can move without the traditional use of motors, cogs, hinges, and other joining corridor. rather, movement and actuation come from the parcels of the accoutrements themselves, for illustration, a single piece of material changing shape upon external stimulants similar as light, pressure, or electrical current. […]
[…] contain more mass than the sun in a space just 10km across. They rotate rapidly and emit intense X-ray radiation. In addition to their mysterious properties, neutron stars may also be composed of new […]